Garden
What Garden Zone Is Texas? Understanding USDA Plant Hardiness Zones
Texas, known for its diverse landscapes and warm climate, presents unique challenges and opportunities for gardeners. Choosing the right plants for your specific area is crucial for success, and that’s where understanding USDA Plant Hardiness Zones comes in.
These zones, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture, are a guide to help gardeners select plants that can thrive in a particular region’s winter temperatures. Texas, with its vast geographical expanse, is home to a variety of these zones, influencing what types of plants can flourish in each area. This article dives into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones in Texas, providing insight into how they impact plant selection, and offering essential tips for successful gardening across the Lone Star State.
Texas’s Distinct Garden Zones
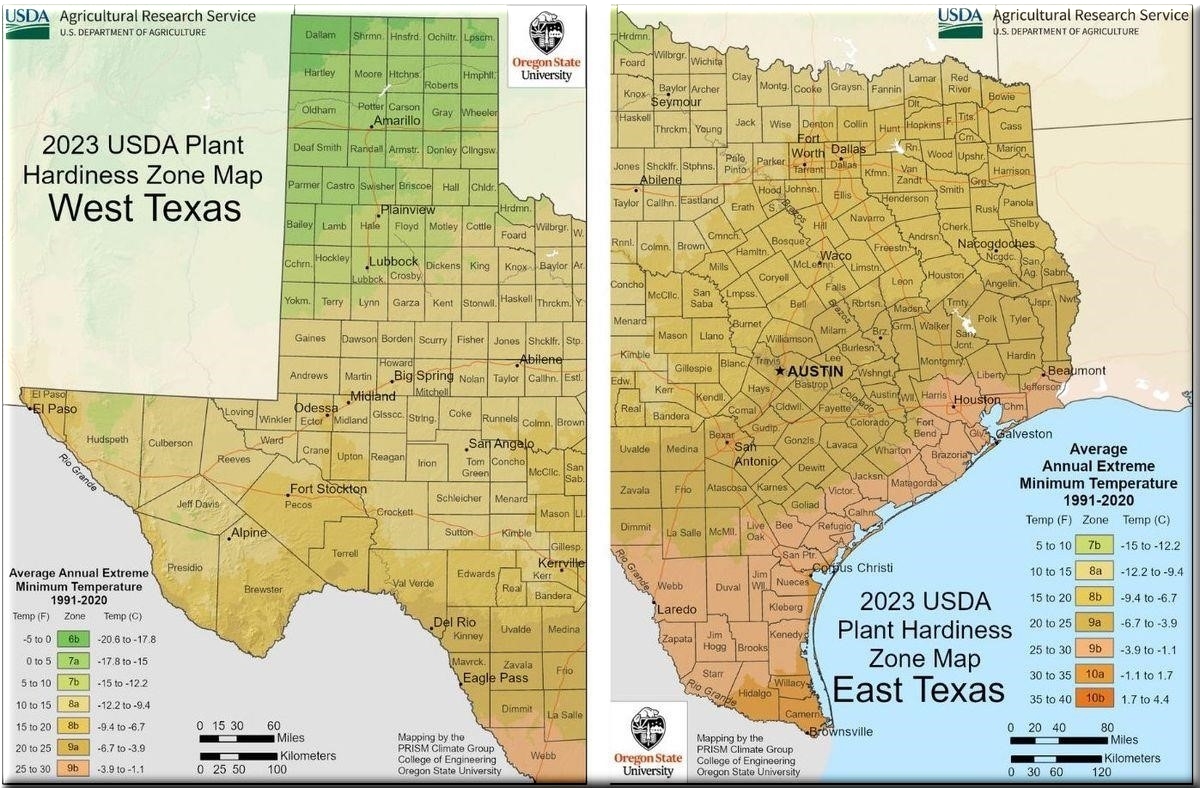
Texas experiences a range of climates, from the cool northern regions to the warm southern tip. This diversity is reflected in the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones that encompass the state. The coolest zone, 6b, is found in northern Texas, while the rest of the state enjoys a warm climate year-round, with zones ranging from 7a to 10b.
Here’s a breakdown of Texas’s USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, along with their typical winter temperature ranges:
- Zone 6b (Northern Texas): Winter temperatures range from -5°F to 20°F.
- Zone 7a: Winter temperatures range from 0°F to 10°F.
- Zone 7b: Winter temperatures range from 5°F to 20°F.
- Zone 8a: Winter temperatures range from 10°F to 20°F.
- Zone 8b: Winter temperatures range from 15°F to 25°F.
- Zone 9a: Winter temperatures range from 20°F to 30°F.
- Zone 10a: Winter temperatures range from 30°F to 40°F.
- Zone 10b: Winter temperatures range from 35°F to 45°F.
It’s important to remember that these zones are just guidelines, and other factors, such as microclimates, can also influence plant survival. Microclimates can be created by elevation, proximity to water, and even the presence of buildings, creating pockets of different temperatures within a single zone.
Factors Beyond Zones: A Deeper Look at Texas Gardening
While USDA Plant Hardiness Zones provide a valuable starting point, other factors play a significant role in plant success. Consider these key aspects when planning your Texas garden:
- Planting Location: The amount of sunlight your garden receives and its exposure to wind can impact plant growth.
- Soil Condition: The pH, drainage, and nutrient content of your soil are crucial for plant health. Testing your soil and amending it as needed can help ensure optimal conditions.
- Humidity: Texas is a relatively humid state, which can affect plant growth. Some plants thrive in humid conditions, while others prefer drier environments.
Finding the Right Plants for Your Texas Garden
Now that you understand USDA Plant Hardiness Zones and other influential factors, you can confidently select plants suitable for your Texas garden.
Here are some resources to help you choose:
- Local Nurseries and Gardening Experts: These professionals can provide invaluable advice tailored to your specific location and gardening goals.
- Online Resources: Websites like coolxtop.com offer a wealth of information on plant selection, care, and gardening techniques.
- Plant Labels: Read plant labels carefully to ensure they are suitable for your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone. They often provide specific recommendations for sun exposure, soil conditions, and other key factors.
Remember, a successful garden starts with choosing plants that are well-suited to your climate, soil, and desired conditions. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different plant varieties to find those that flourish in your Texas garden.
Gardening Resources in Texas
Texas is a state with a passionate gardening community, offering a wealth of resources for both beginners and experienced enthusiasts. Here are some excellent starting points:
- Local Gardening Clubs and Organizations: These groups provide a supportive environment for exchanging knowledge, sharing tips, and getting hands-on experience.
- State University Extension Services: Texas A&M AgriLife Extension offers a vast array of educational programs and publications on gardening, pest control, and more.
- Online Forums and Communities: Several online platforms connect gardeners across the state, allowing you to ask questions, seek advice, and share your own experiences.
- Government Agencies: The Texas Department of Agriculture offers information on native plants, sustainable practices, and other gardening resources.
Tips for Successful Texas Gardening
Gardening in Texas is a rewarding experience, offering a wide range of plants to grow. Here are some general tips to help you achieve success:
- Water Wisely: Texas is known for its hot summers, so proper watering is critical. Use a drip irrigation system or hand watering techniques to minimize water waste.
- Fertilize Properly: Texas soils can be depleted of nutrients, so regular fertilization is important. Use a slow-release fertilizer to provide a steady supply of nutrients for your plants.
- Maintain Regularly: Keep your garden tidy by removing weeds, dead leaves, and any diseased plants. This helps prevent the spread of pests and diseases.
- Protect from Extreme Weather: Texas experiences both heat waves and occasional freezes. Take steps to protect your plants during these extreme weather events, such as providing shade, using frost blankets, or bringing potted plants indoors.
FAQs
What are the winter temperatures in Texas?
Winter temperatures in Texas vary significantly depending on the location. Northern Texas experiences the coldest temperatures, with lows ranging from -5°F to 20°F. As you move southward, temperatures become milder, with average lows ranging from 20°F to 45°F.
How does elevation affect plant hardiness in Texas?
Higher elevations tend to experience cooler temperatures than lower elevations, even within the same USDA Plant Hardiness Zone. This means that a plant that might thrive at a lower elevation might not be suitable for a higher elevation within the same zone.
Where can I find a map of Texas’s USDA Plant Hardiness Zones?
You can find a map of Texas’s USDA Plant Hardiness Zones on the official USDA website.
What are some of the best plants for beginners in Texas?
Texas offers a diverse range of plants suitable for beginners. Consider these options:
- Flowers: Zinnias, cosmos, sunflowers, and coreopsis are easy to grow and produce vibrant blooms.
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, beans, and herbs like basil and oregano are good choices for Texas gardens.
- Trees: Texas red oak, live oak, and pecan trees are drought-tolerant and add beauty to your landscape.
What are the challenges of gardening in Texas?
Texas presents some unique challenges for gardeners, including:
- Extreme Heat: Summer temperatures can be extremely hot, requiring careful watering and shade for some plants.
- Drought: Texas experiences periodic droughts, making water conservation crucial.
- Pests and Diseases: Texas is home to a variety of pests and diseases that can affect plants.
Conclusion
Knowing your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone in Texas is a crucial step towards creating a thriving garden. By understanding the different zones and their associated temperature ranges, you can make informed plant selections and ensure that your garden flourishes in Texas’s diverse climate. Remember, gardening is a rewarding journey of learning and experimentation. Don’t hesitate to seek advice from local experts, consult reliable resources, and share your experiences with other gardeners. Happy gardening!

Leave a Reply