Garden
The Right Soil for Your Raised Garden Beds: Choosing the Perfect Mix
If you’re building a raised garden bed, you’re in for a rewarding experience. But before you start planting, let’s talk about the most important element: the soil. Selecting the right soil mix for your raised beds is crucial for successful gardening. Just like a house needs a strong foundation, your plants need a healthy, nutrient-rich soil to thrive. This article will guide you through the key elements of choosing the perfect soil mix for your raised garden, ensuring you have a foundation for flourishing plants and bountiful harvests.
Choosing the Right Soil Mix for Your Raised Garden Beds
Why is the right soil so important? Think of it like this: your plants need a comfortable home, and that home is the soil. It provides them with the nutrients, water, and structure they need to grow strong and healthy. A well-chosen soil mix will encourage strong root systems, prevent drainage problems, and create a vibrant environment for your plants to flourish.
You can purchase generic potting soil, but crafting a custom soil mix for your raised beds offers numerous advantages. You can tailor it to the specific needs of your chosen plants, ensuring they have the perfect environment to grow. A custom mix also helps to boost soil health and fertility, which means you’ll be less reliant on chemical fertilizers and more likely to have thriving plants over the long term.
What are the Key Ingredients?
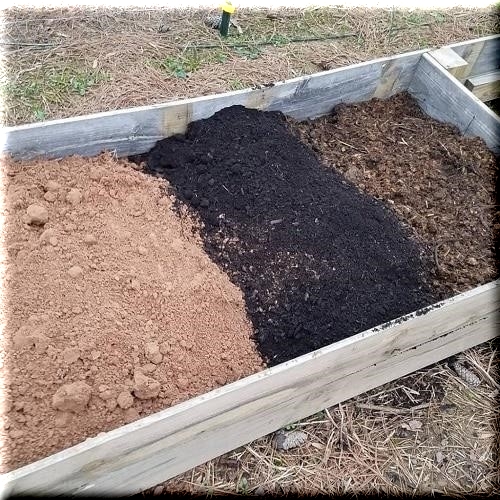
Compost: Compost is the foundation of a good raised bed soil mix. It’s rich in nutrients, improves soil structure, and encourages healthy microbial activity. It’s like adding a natural boost of energy to your soil! You can make your own compost from kitchen scraps and yard waste, or purchase high-quality compost from a local supplier.
Topsoil: Topsoil, the upper layer of soil, is another important component. It’s generally rich in minerals and nutrients, adding structure and a good foundation to your soil mix. Choose a topsoil that is free from contaminants and has a good balance of nutrients.
Peat Moss: Peat moss is often included in raised bed soil mixes because it has excellent water retention properties. It helps to create a consistent moisture level, keeping your plants hydrated without becoming waterlogged. It’s crucial to consider that peat moss is a non-renewable resource, so using alternatives like coco coir or composted bark is becoming increasingly popular.
Vermiculite: Vermiculite is a lightweight, airy material that improves drainage and aeration in soil. It helps the soil hold moisture without becoming too dense, creating a healthy environment for root growth.
Other Amendments: Depending on your plants’ needs, you might also add worm castings (an excellent source of nutrients), aged manure (adding organic matter and nutrients), or bark (which helps with drainage and aeration).
Understanding the Needs of Your Plants
To choose the perfect soil mix, you need to understand the specific needs of your plants. Different plants thrive in different soil conditions, so let’s explore a few key factors:
pH Levels: Soil pH measures its acidity or alkalinity. Most vegetables prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (around 6.0 to 7.0). You can test your soil’s pH using a home kit or send a sample to a lab for analysis. Adjusting pH levels can be achieved by adding lime to increase alkalinity or sulfur to increase acidity.
Nutrients: Plants need a variety of essential nutrients to grow properly. Some plants are heavy feeders, requiring more nutrients than others. You can conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels in your soil or use a soil amendment to add specific nutrients.
Drainage and Aeration: Good drainage is essential for healthy root development. The soil should allow excess water to drain away, preventing roots from becoming waterlogged. Aeration is also important, ensuring that air can circulate through the soil, allowing roots to breathe.
Popular Raised Bed Soil Mix Recipes
Now that you have a better understanding of the basics, let’s explore some popular raised bed soil mix recipes:
Mel’s Mix (1/3 Peat Moss, 1/3 Vermiculite, 1/3 Compost): This recipe, popularized by Mel Bartholomew’s Square Foot Gardening, is known for its excellent drainage and water retention. The peat moss helps create a fluffy, airy texture, while the compost provides the essential nutrients for healthy plant growth. This mix is particularly suitable for vegetables and herbs.
"Perfect Soil Recipe" (50% Topsoil, 30% Compost, 20% Other Organic Matter): This recipe is another favorite, often recommended by gardening experts. The blend of topsoil and compost provides a solid foundation for healthy growth, while the additional organic matter adds further structure and nutrients.
DIY Custom Mix: Experimenting with different combinations is a great way to personalize your soil mix to meet specific plant needs. You can adjust the ratios of compost, topsoil, and peat moss based on your preferred drainage, aeration, and nutrient requirements.
Tips for Success
Testing Your Soil: It’s always a good idea to test your soil, especially if you’re new to gardening. A soil test will give you a comprehensive overview of your soil’s pH, nutrient levels, and drainage. You can purchase a simple soil test kit or send a soil sample to a lab.
Making Adjustments: Once you have your soil test results, you can make adjustments to your soil mix. If your soil is too acidic, you can add lime. If your soil lacks nutrients, you can add fertilizer or amendments like worm castings or bone meal.
Maintaining Soil Health: To keep your soil healthy and productive, it’s important to amend it regularly. You can add compost each year, layer mulch to protect the soil, and rotate crops to prevent nutrient depletion.
Alternatives to Traditional Soil Mixes
No-Till Raised Beds: No-till gardening is a method that minimizes soil disturbance. Instead of tilling the soil, you add compost and other amendments directly to the surface, creating a healthy ecosystem for your plants. This approach is gaining popularity as it promotes soil health, reduces erosion, and enhances biodiversity.
Living Soil: Living soil focuses on building a thriving ecosystem within your soil. It encourages a healthy population of beneficial microbes, fungi, and insects that contribute to nutrient cycling and soil fertility. This approach emphasizes using organic materials, minimal soil disturbance, and promoting a diverse and balanced microbial community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of raised bed soil is best for tomatoes?
Tomatoes thrive in well-draining soil with a pH of 6.0 to 6.5. A mix of compost, topsoil, and a small amount of peat moss or coco coir works well.
How do I make my soil mix more nutrient-rich?
You can enhance nutrient levels by adding compost, aged manure, worm castings, or bone meal to your soil mix. These amendments provide a natural boost of essential nutrients.
Can I use regular potting soil in my raised beds?
You can, but custom soil mixes tend to provide better drainage and aeration for root health. Potting soil is often designed for container gardening and may not be ideal for raised beds.
Conclusion
Finding the right soil for your raised beds is the cornerstone of successful gardening. By understanding the needs of your plants, experimenting with different soil mixes, and adopting best practices for maintaining soil health, you’ll create a thriving garden environment for your plants to flourish.
Remember, gardening is a journey of discovery. Explore different techniques, experiment with soil mixes, and keep learning. Let’s connect! Share your favorite soil mix recipes or tips in the comments below.


Leave a Reply